Since its inception, the high-pressure die casting process has experienced substantial advancements, evolving from a primitive process into a contemporary, highly efficient, and technologically advanced manufacturing method. The growth and progress of die casting helped improve the competitiveness of various industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to electronics and consumer goods.
In this blog, we will explore the journey of die casting, from its humble beginnings to the cutting-edge techniques used today.
The Birth of Die Casting
Die casting can trace its origins back to the mid-19th century when it was first developed to produce printing typefaces. This early die casting process involved manually pouring molten metal into a reusable die. The dies were typically made of iron or bronze, and the process was labor-intensive, slow, and unsuitable for mass production.
The Advent of Cold-Chamber Die Casting
The limitations of this early gravity poured die casting process, including the inability to use high-melting-point metals like aluminum and reduced die life due to the corrosive effects of molten zinc and lead, led to the development of cold-chamber die casting in the early 20th century. In this method, the molten metal is ladled into a separate chamber before being injected into the die. This innovation allowed for a more comprehensive range of metals and alloys and improved safety for workers.
The Rise of High-Pressure Die Casting
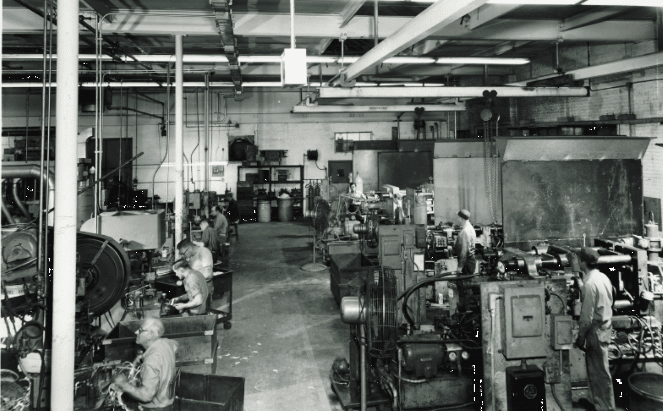
As technology advanced, the die casting process evolved further with the emergence of high-pressure die casting (HPDC). This technique employs hydraulic or mechanical pressure to inject molten metal into the die at significantly higher speeds and pressures. HPDC enables the production of thinner and more intricate parts with improved mechanical properties. Aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys are commonly used in HPDC due to their fluidity, high strength-to-weight ratios, and stability.
The Influence of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Simulation Technology
In the modern era, computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation software have played a pivotal role in the die casting process. Engineers can now design complex dies and simulate the casting process to identify potential issues and optimize designs before production begins. This technology reduces the development time, minimizes material wastage, and ensures better final product quality.
Automation Then vs. Now
The mid-20th century saw a significant shift in die casting with the introduction of automated systems. These advancements allowed for greater consistency, speed, and cost-effectiveness in production. Automatic machines became capable of producing complex parts with high precision at a high rate of speed.
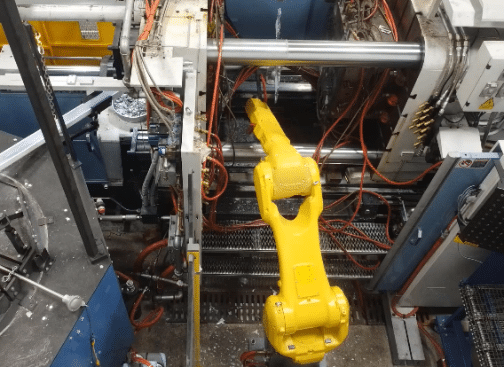
In the 21st century, we have integrated advanced robotic systems into the die casting processes itself – streamlining operations and significantly reducing manual labor. These automated systems excel in tasks like metal injection and part extraction, ensuring a higher consistency and quality in the final products. Additionally, integrating smart technologies and real-time monitoring systems allows for better control over the production line, enabling quick adjustments and minimizing downtime. As a result, die casting operations today benefit from increased productivity, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to meet the growing demand for complex and high-precision components in various industries.
Modern Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices
Today, sustainability is a driving force in manufacturing, and die casting is no exception. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as using recycled materials, optimizing energy consumption, and reducing waste in the die casting process.
Die casting produces components with high precision and dimensional accuracy. Lightweight, high-pressure die castings made from aluminum or magnesium often serve as replacements for steel or iron parts, leading to improved energy efficiency in products. Additionally, die casting machinery is designed for energy efficiency, further reducing the carbon footprint of the manufacturing process.
The Future of High-Pressure Die Casting
The evolution of high-pressure die casting from traditional methods to the modern, highly advanced processes we see today is a testament to human innovation and the relentless pursuit of efficiency and quality in manufacturing. Die casting has gone from a labor-intensive, slow process to a high-speed, automated, and sustainable method capable of producing intricate, high-quality components for various industries. As technology advances, we expect die casting to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
Learn more about the high-pressure die casting process here. Click here to request a quote, or click here to contact Chicago White Metal.






