Die casting and sand casting are two popular methods for manufacturing metal parts. While both methods involve casting liquid metal in a mold to create a product or part, there are significant differences between the two processes.
What is Die Casting?
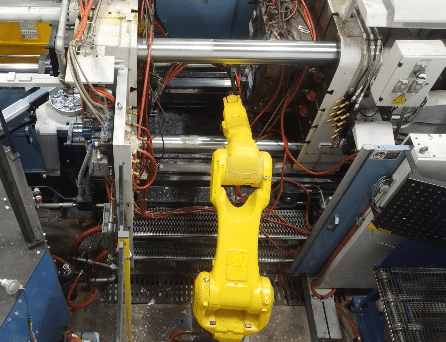
Die casting is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten metal into a complex, highly engineered multi-component steel mold, or “die,” that is set in a machine that controls the clamping, metal injection, die opening, part ejection/extraction, die cooling, and lubrication processes. Die casting can be used with various metals, including aluminum, magnesium, and zinc. Each metal has unique properties and benefits (learn about them here), suitable for countless applications.
Die casting uses sophisticated hydraulics to inject molten metal into the steel die with tremendous speed and pressure. The machines can apply hundreds of tons of locking force to hold the die shut during metal injection. The water-cooled die extracts the heat, causing the metal to solidify quickly – this process can run up to 100 cycles or more per hour. The machine then opens the die. The part is automatically ejected and (typically) placed into a trim die where the excess material is sheared away, leaving a near-net-shaped part. In some die casting processes, “in die” de-gating separates the excess material from the part resulting in a net shape part produced directly from the casting process.
Automated systems then cool and lubricate the die surface after each cycle.
What is Sand Casting?

Sand casting is a metal casting process that uses sand as the mold material to create parts. This process is best suited for low-volume production.
Molten metal is poured into the cavity through a sprue channel. The metal fills the cavity and takes on the shape of the part. Once the metal has cooled and solidified, the sand mold is broken apart to reveal the casting. Excess material is then removed from the casting by band sawing and grinding.
Advantages of Die Casting
Here are some benefits of die casting over sand casting:
- Precision: Die casting produces parts with tighter tolerances, thinner walls, and lower draft which results in less secondary machining compared to sand casting.
- Surface finish: Die casting provides a smoother surface finish than sand casting.
- Efficiency: Die casting is a faster and more efficient process resulting in lower part cost.
While sand casting has advantages for certain applications, die casting allows for faster production rates, lower labor costs, and the ability to produce more complex shapes and thinner walls – making it a popular choice for high-volume applications. If you think that die casting might be the right fit for your project, contact us today. You can also request a quote here.







