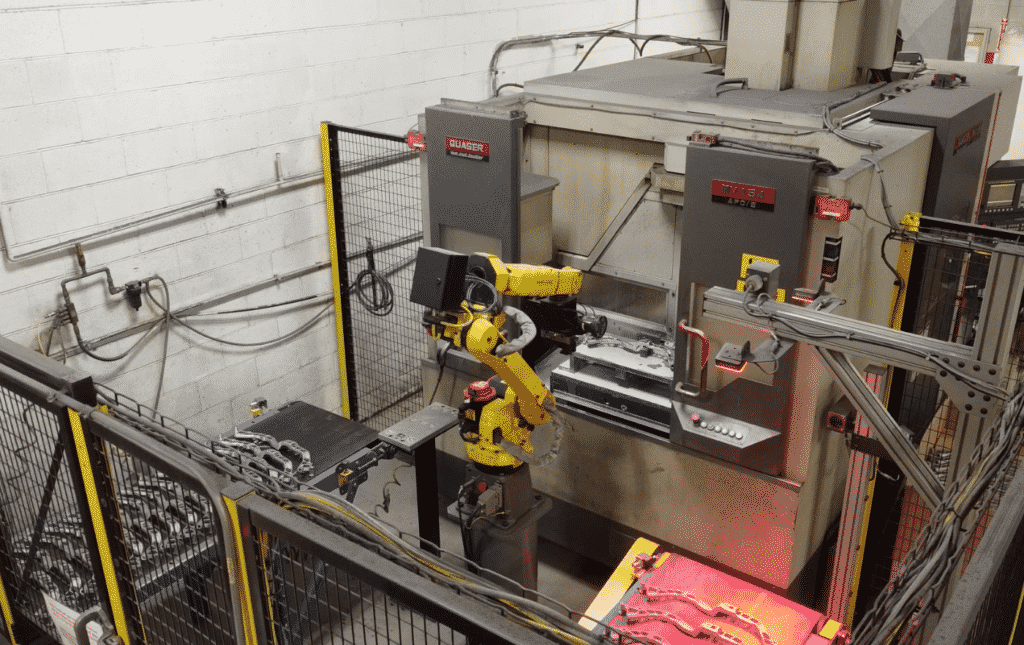
Past vs. Present
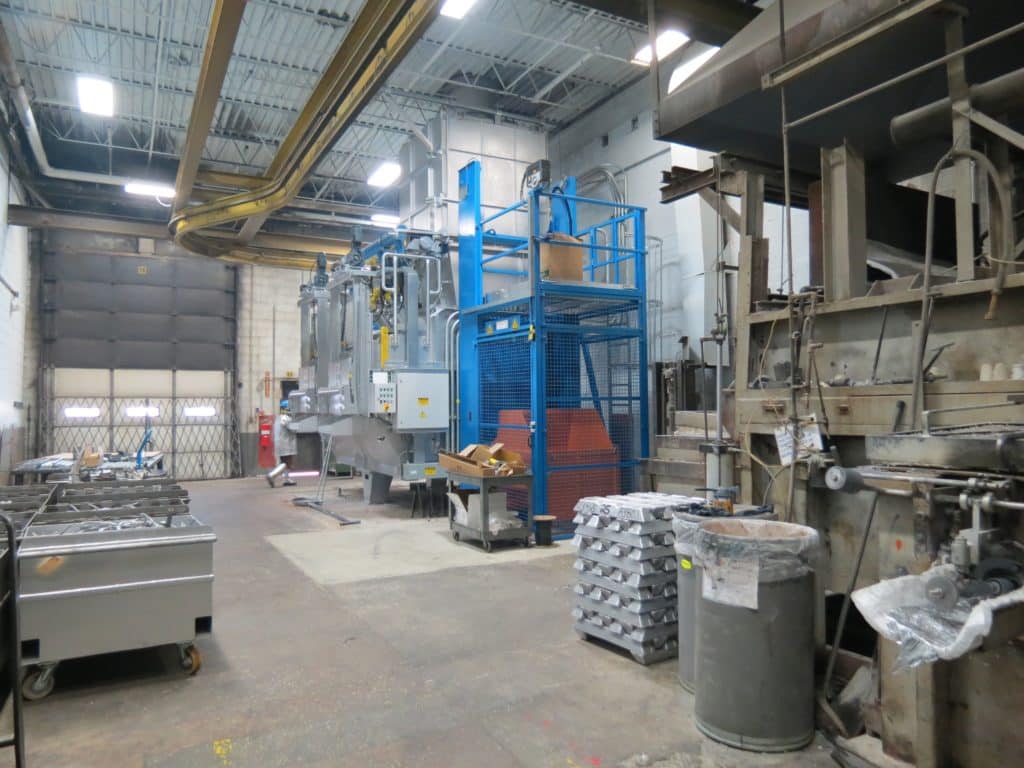
In the past, a manufacturer might have only been able to produce a small number of parts per day. Machinery advancements enabled output to increase. For example, the first documented use of the die casting process was in the mid-19th century. It involved manually pouring molten metal into a die that opened and closed using a primitive machine. Today’s manufacturers, when employing state-of-the-art machinery and a skilled team, can produce thousands of units per day, if not more.
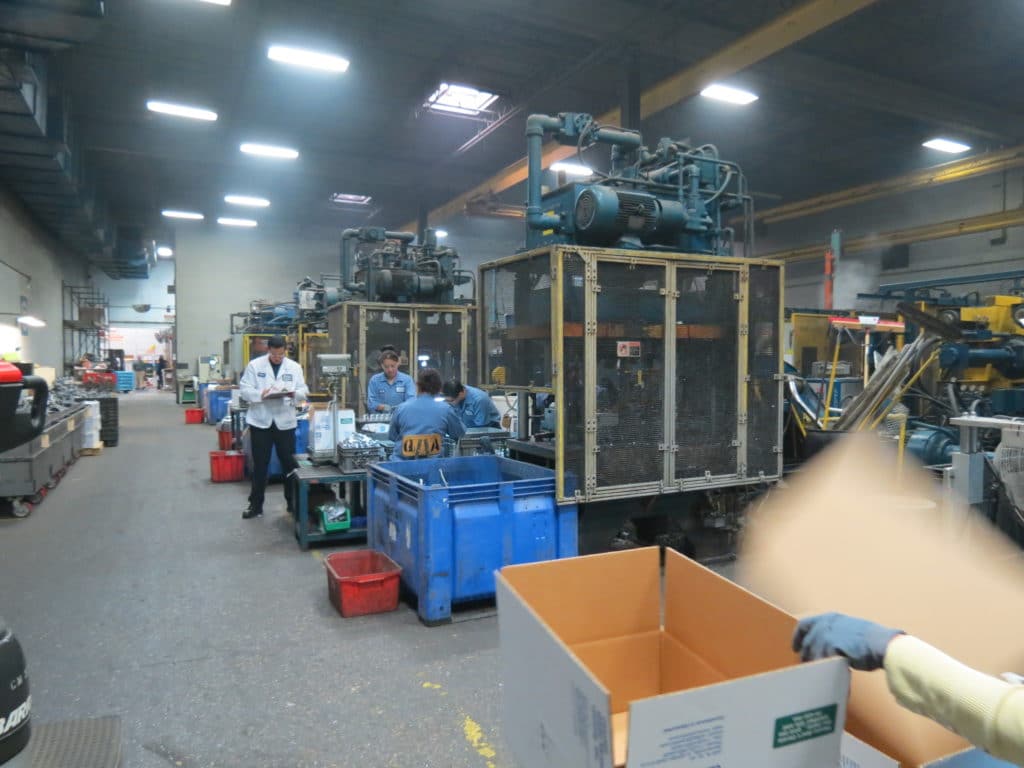
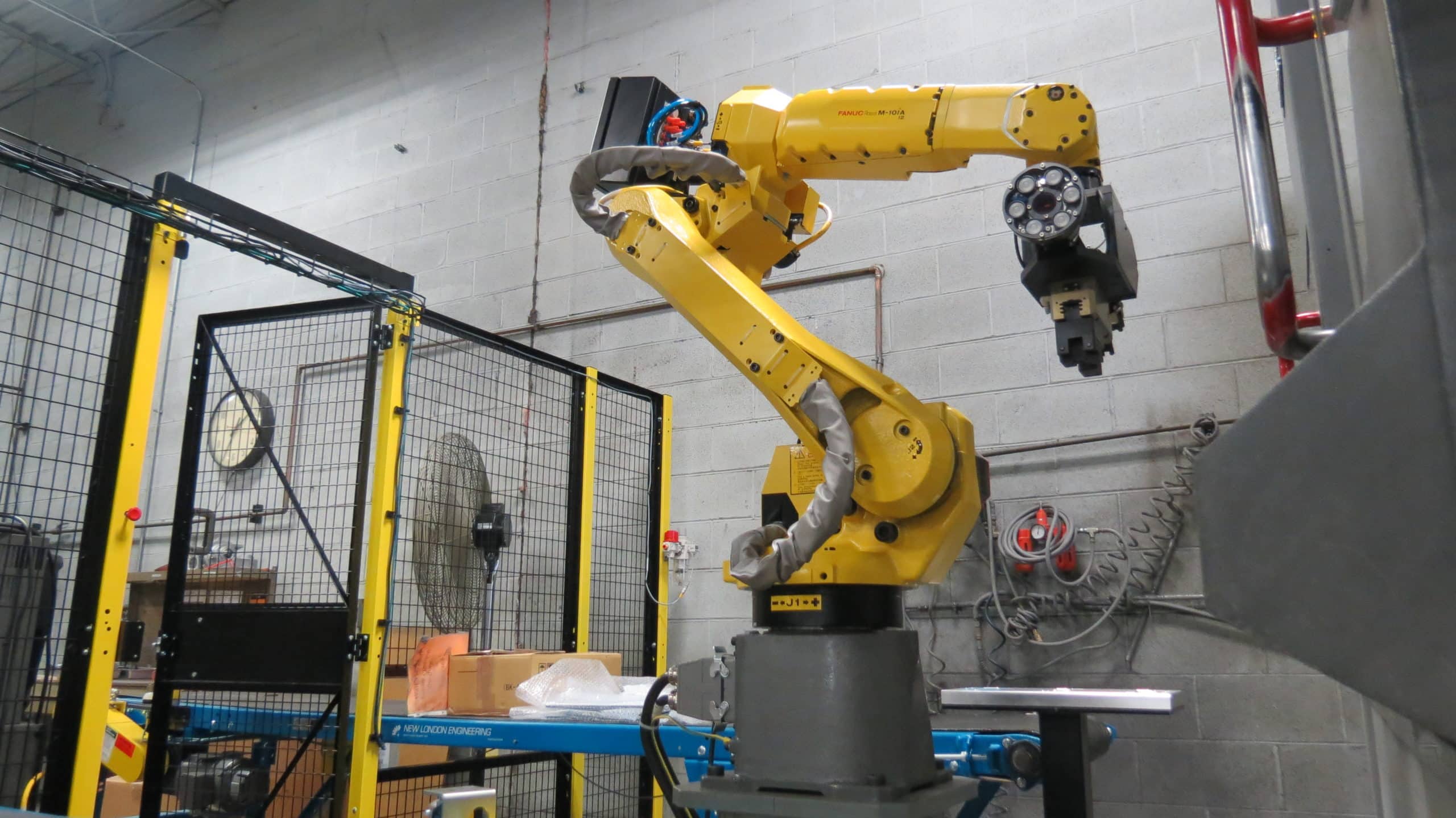
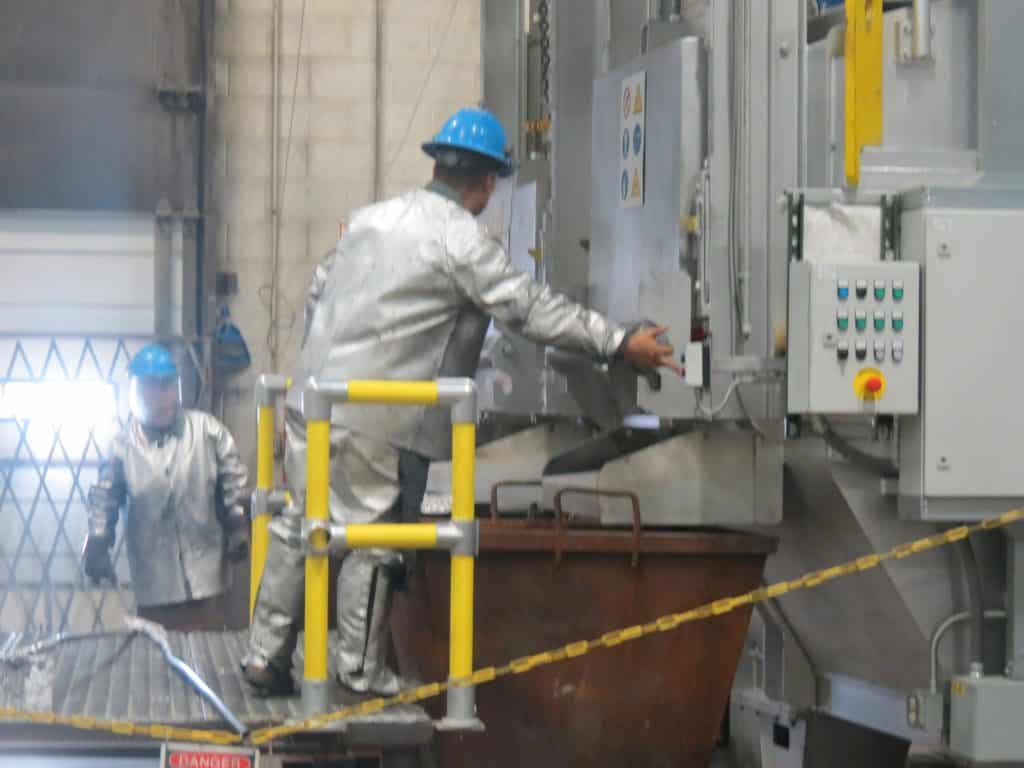
Modern high-volume die casting takes advantage of automation, including robotics, sophisticated controls, camera systems, sensors, and other technical advancements. These innovations offer many benefits, including repeatability, higher quality products, and lower (and more predictable) long-term costs of operation. However, successfully scaling to high-volume manufacturing requires foresight and planning to streamline the production process and minimize changes.
Scaling – Best Practices
Scaling up a product from the prototype or low-volume production stage (such as a machined part) to a high-volume manufacturing environment (such as high-pressure die casting) can be one of the most exciting stages of the production process. The decisions made during this transition will have significant implications for all aspects of a product, from tooling and manufacturing process control, to packaging and user documentation. That’s why it’s crucial to have an experienced team around you to help guide you through the process.
Here are some questions to ask yourself before considering scaling up to a high-volume manufacturing process such as high-pressure die casting:
- Are you confident you’ll need enough parts to justify the tooling investment required for high-pressure die casting?
- The typical quantity for high-pressure die casting is 5,000 pieces per year for several years (often much higher). There are exceptions, but the higher the volume, the more likely the high-pressure die casting process would be the right choice for your product.
- Will the alloy offered by the die caster be suitable for your application?
- Some of the more common die casting alloys include A380 aluminum, AZ91D magnesium, and Zinc #3.
- Ferrous alloys are not an option for high-pressure die casting.
- Is your design appropriate for high-pressure die casting?
- Die casting is more likely to be the right choice if the design is three-dimensional and not easily stamped or extruded.
- Is the design optimized and stable?
- In order to maximize the payback from the tooling investment, it’s crucial to optimize the design and be sure that it is relatively stable before building tooling, as making changes to tooling after it is constructed can be expensive.
Partnering with the Right Die Caster
If you think your part is eligible for high-pressure die casting, it’s vital to seek out a reputable die caster who has enough experience to guide you through the process of selecting an appropriate alloy, optimizing the design, building robust high-quality tooling, and developing an optimized set of processing parameters. There are numerous areas where an experienced die caster can help your organization ramp up to higher-volume production.

When you collaborate with a die caster who utilizes this state-of-the-art technology, it ensures that your part is manufactured efficiently over the entire product lifecycle – that’s why it’s essential to have a team of experts available to work with you throughout the process.
CWM & High-Volume Production
CWM’s approach to high-volume production is the same in all we do: Excellence is expected. Our engineering and manufacturing processes are streamlined to benefit our customers’ needs. For example, if high-pressure die casting makes sense, we will provide accurate estimates of the cost of tooling and parts, including complete finishing, coatings, etc., and we will work with your team to make sure the part is a success.
Chicago White Metal specializes in high-volume production of Aluminum, Magnesium, and Zinc die cast parts. We supply numerous industries with parts that are used in everyday products across the world. Don’t hesitate to contact us if you want to learn more about our high-volume die casting services.


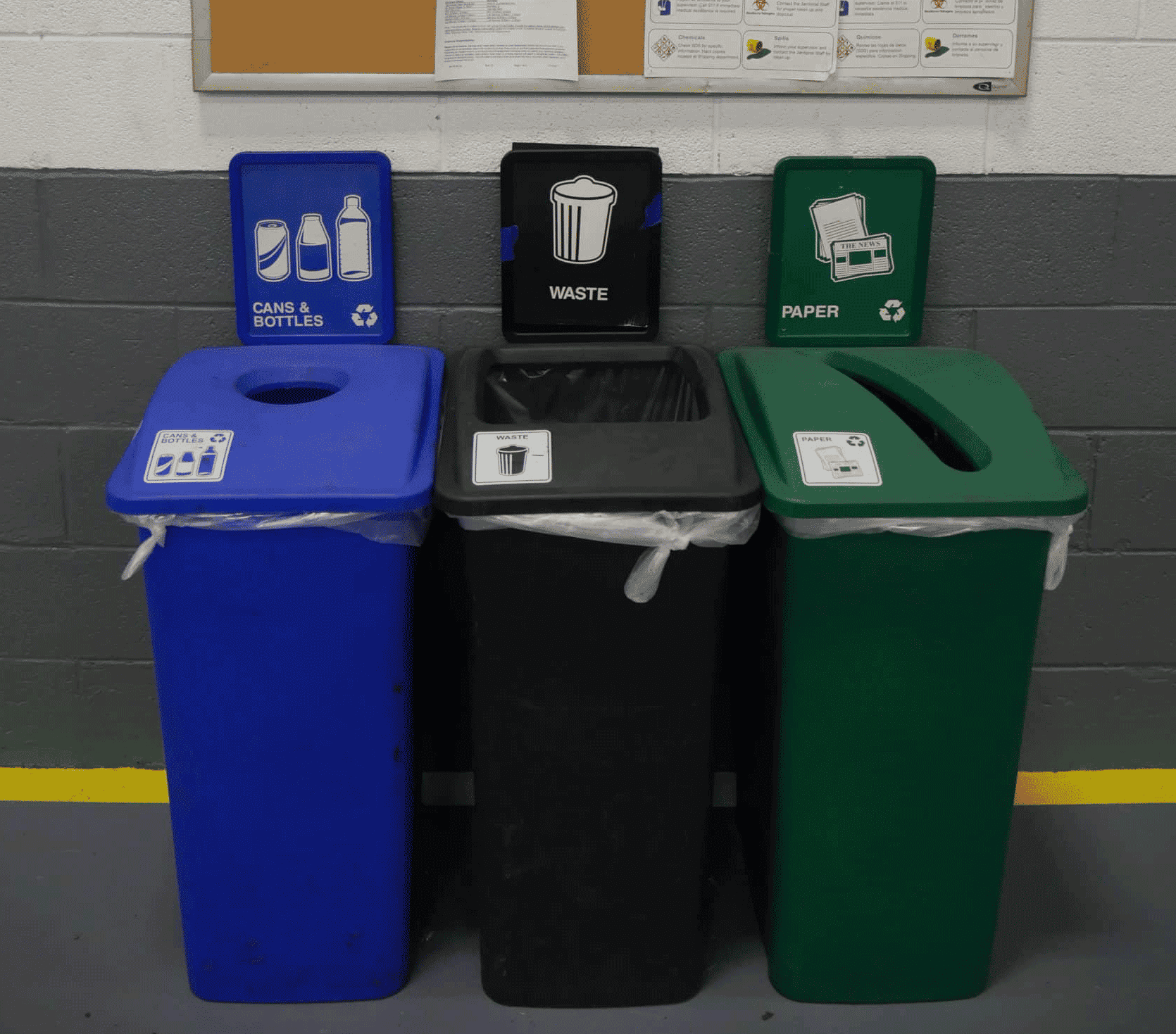
 Chicago White Metal’s environmental practices began long before cultural demands for sustainability started. Reduce, Reuse, Recycle has always been the mantra throughout our operations and supply chain. In both our plant and office operations, recycling comes first.
Chicago White Metal’s environmental practices began long before cultural demands for sustainability started. Reduce, Reuse, Recycle has always been the mantra throughout our operations and supply chain. In both our plant and office operations, recycling comes first.
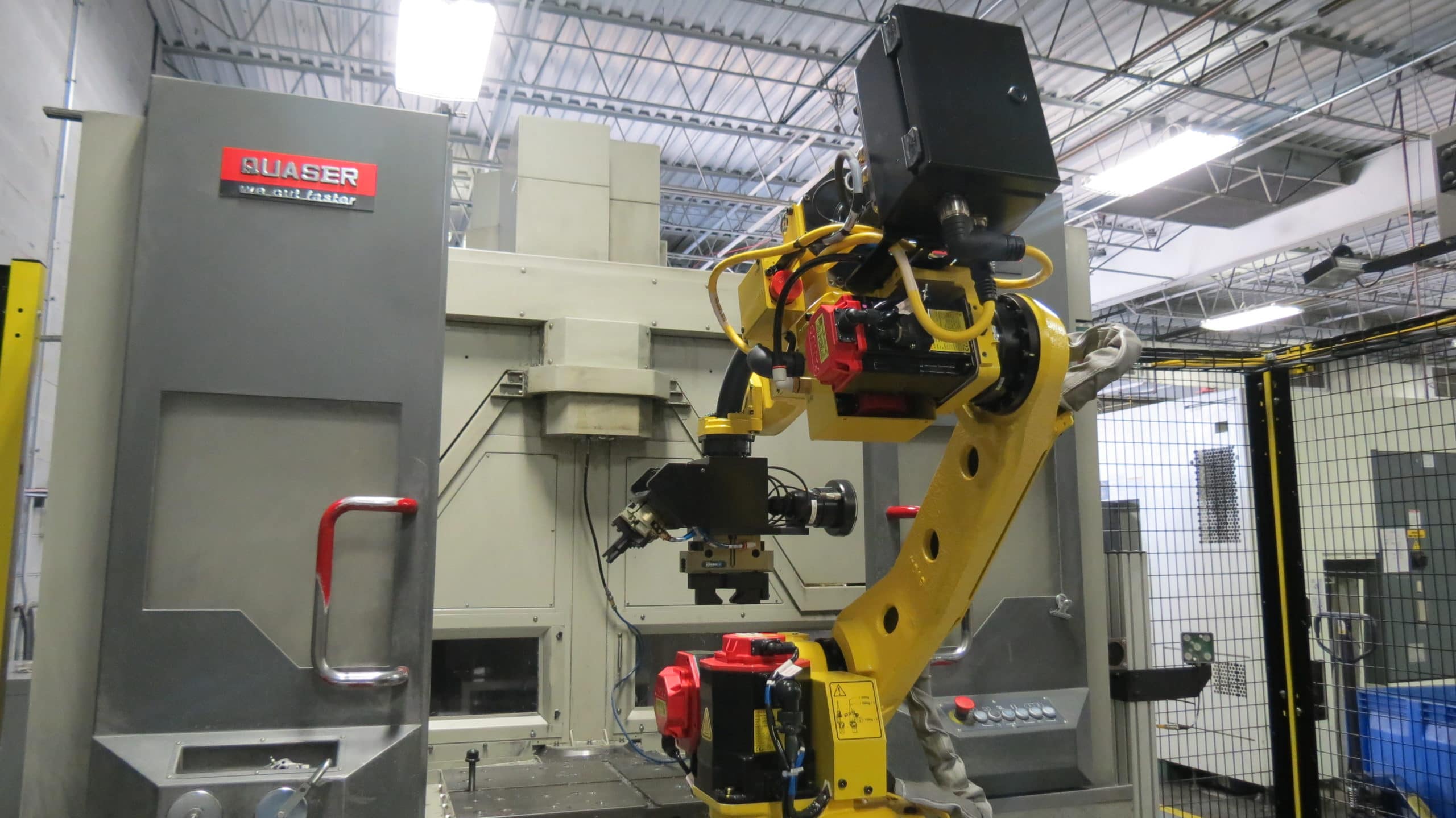
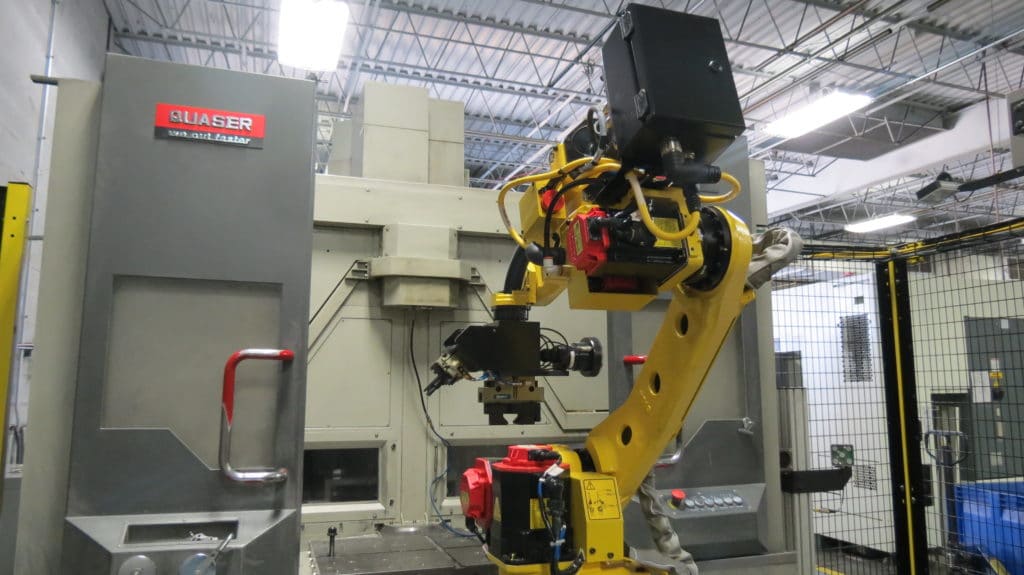



 Before the Design for Manufacturing (DFM) process can begin, it’s essential to determine which manufacturing process will be the optimal solution for your final product. While several methods are available to manufacture parts efficiently, few offer the quality, environmental advantages, and cost savings of die casting.
Before the Design for Manufacturing (DFM) process can begin, it’s essential to determine which manufacturing process will be the optimal solution for your final product. While several methods are available to manufacture parts efficiently, few offer the quality, environmental advantages, and cost savings of die casting. CWM welcomes video conferences throughout the process and encourages face-to-face meetings on-site at CWM, or we can arrange for our team to visit your location. A visit to CWM will allow both our team and your team to develop a partnership, review best practices, learn about the die casting process & other technologies used at CWM, and discuss the plans for the future.
CWM welcomes video conferences throughout the process and encourages face-to-face meetings on-site at CWM, or we can arrange for our team to visit your location. A visit to CWM will allow both our team and your team to develop a partnership, review best practices, learn about the die casting process & other technologies used at CWM, and discuss the plans for the future.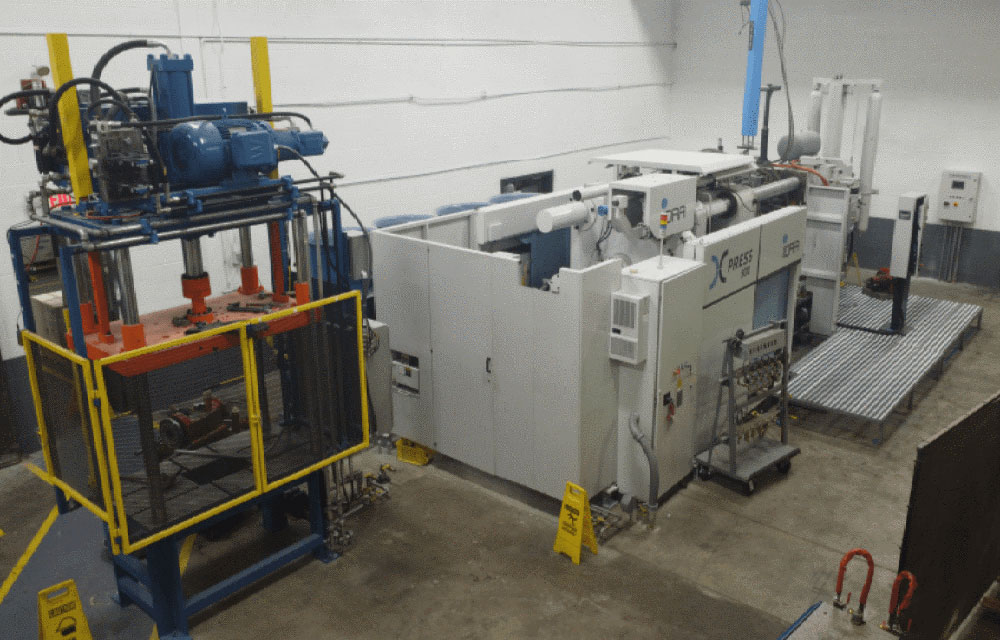
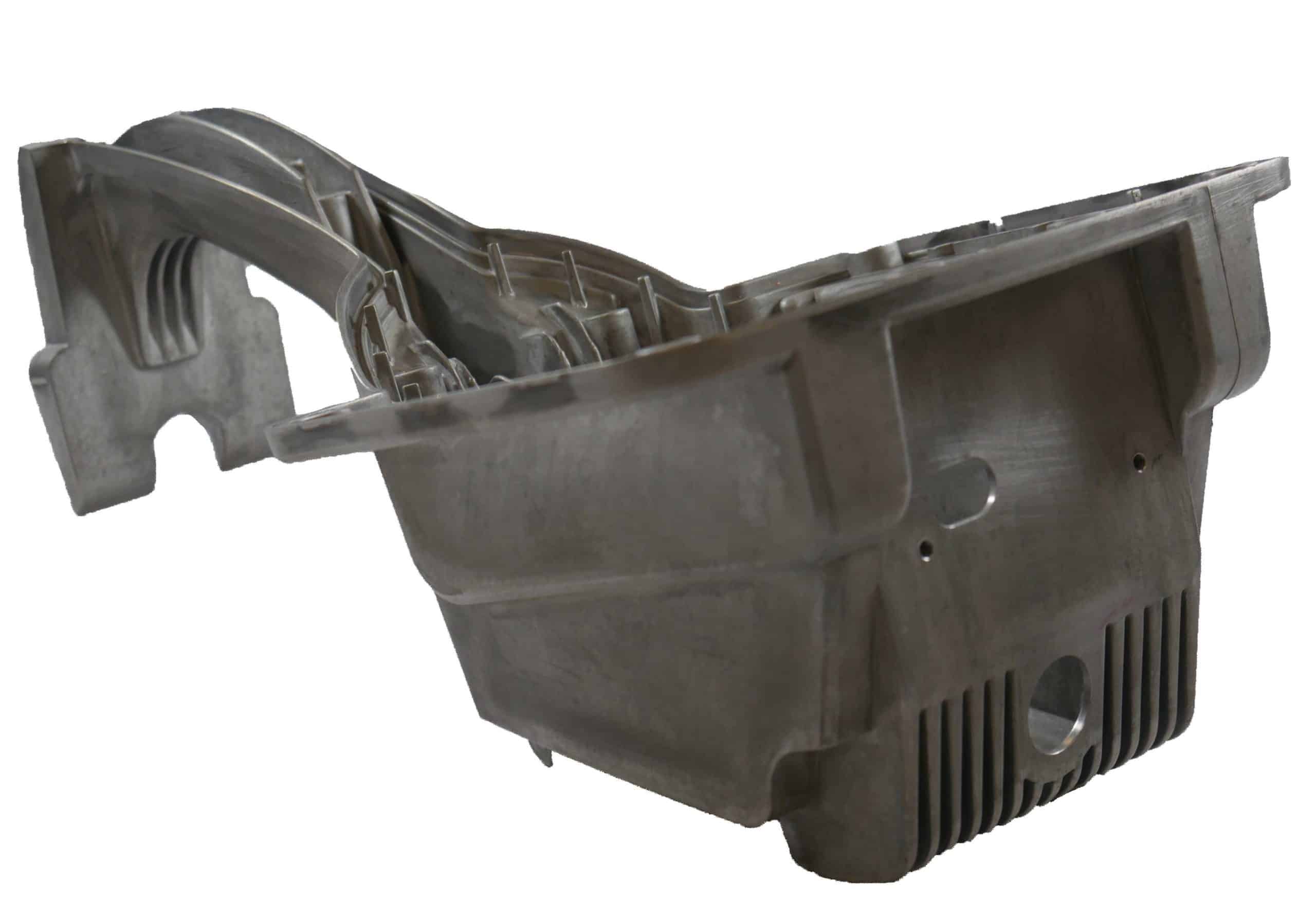


 The International Magnesium Association has awarded Chicago White Metal in conjunction with Waygate Technologies with its 2021 IMA Award of Excellence in its Commercial (non-automotive) Cast Product!
The International Magnesium Association has awarded Chicago White Metal in conjunction with Waygate Technologies with its 2021 IMA Award of Excellence in its Commercial (non-automotive) Cast Product!